6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro
When a tiny, helpless kitten depends entirely on human care for survival, every feeding becomes a life-or-death moment that can make the difference between thriving and failure. Whether dealing with orphaned kittens, rejected babies, or supplementing a mother cat’s insufficient milk supply, mastering the art of bottle feeding requires precision, patience, and professional-level knowledge that many well-meaning caregivers lack.

Learning these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro can transform anxious feeding sessions into confident, successful experiences that give vulnerable kittens the best possible start in life. These proven techniques, developed by veterinary professionals and experienced kitten foster caregivers, address the most critical aspects of newborn kitten nutrition and feeding safety.
Key Takeaways
- Use only kitten-specific formula heated to 98-102°F and never cow’s milk or human infant formula
- Feed kittens in belly-down position at 45-degree angle every 2 hours for optimal safety and digestion
- Follow precise feeding amounts based on age and weight, starting with 2-6 mL for 0-1 week old kittens
- Never force feeding or squeeze bottles as this creates dangerous aspiration risks
- Maintain sterile feeding equipment and use distilled water for formula preparation
Understanding Newborn Kitten Nutritional Needs
Newborn kittens arrive in the world completely dependent on their mother’s milk for survival. When circumstances prevent natural nursing, understanding their unique nutritional requirements becomes absolutely critical for successful hand-rearing.
Critical Feeding Windows
Unlike human babies who can go several hours between feedings, newborn kittens require frequent, consistent nutrition to maintain their blood sugar levels and support rapid growth. Their tiny stomachs and fast metabolisms demand feeding schedules that mirror natural nursing patterns.
Kittens aged 0-1 week require 2-6 mL of formula every 2 hours, while those 1-2 weeks old need 6-10 mL every 2-3 hours[3]. This intensive schedule continues around the clock, making kitten care a demanding but rewarding responsibility.
Formula Requirements
Never use cow’s milk or human infant formula for kittens, as these can cause severe digestive upset and nutritional deficiencies[3]. Kittens require specially formulated kitten milk replacer that matches the protein, fat, and nutrient profile of mother cat’s milk.
The general guideline suggests approximately 8 milliliters of formula per ounce of body weight per day[1], though individual kittens may need slight adjustments based on their growth rate and appetite.
1. Choose the Right Formula and Prepare It Properly
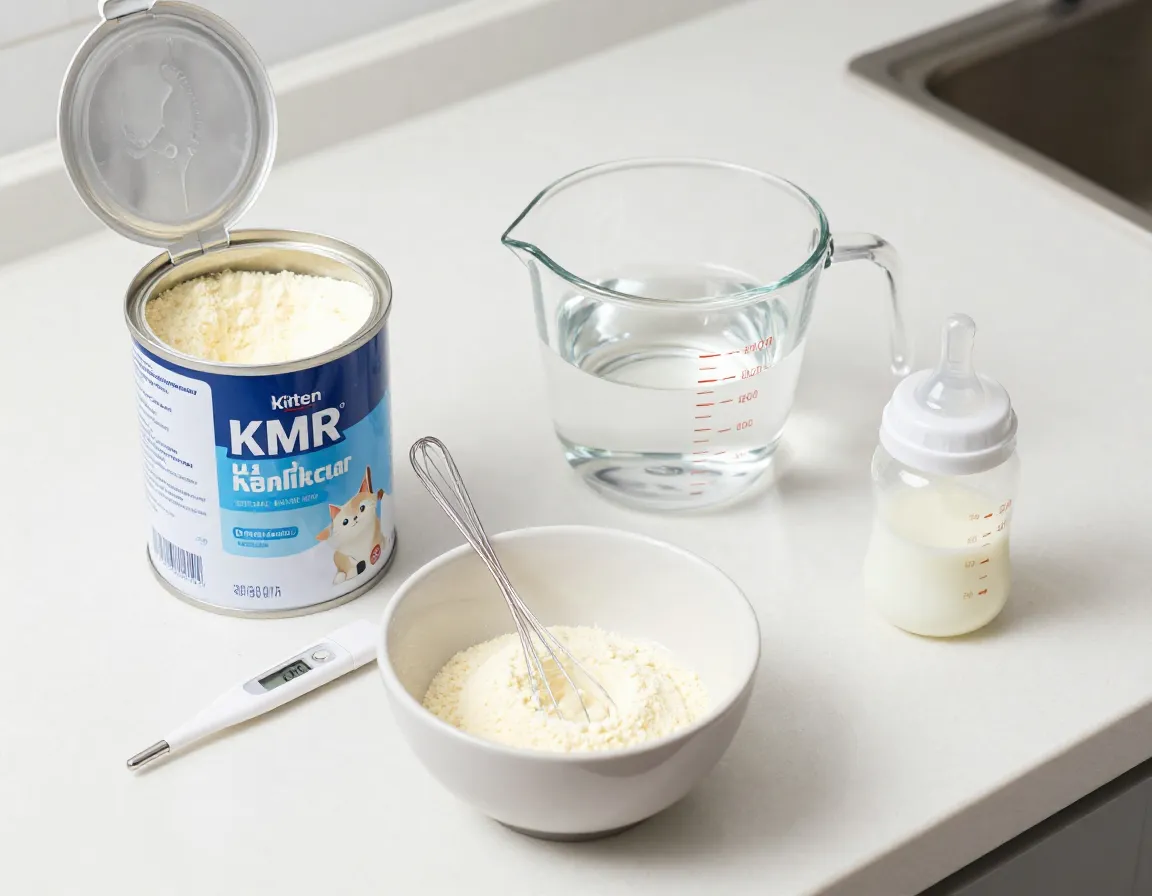

The foundation of successful kitten bottle feeding starts with selecting appropriate formula and preparing it with professional precision. This first tip among the 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro can prevent digestive issues and ensure optimal nutrition.
Selecting Quality Kitten Formula
Commercial kitten milk replacers provide the closest nutritional match to mother cat’s milk. Look for products specifically labeled for kittens that contain:
- High-quality proteins for muscle development
- Essential fatty acids for brain and eye development
- Vitamins and minerals in appropriate ratios
- Prebiotics for digestive health
Popular brands include KMR (Kitten Milk Replacer), Esbilac, and PetAg, all formulated to meet the unique needs of growing kittens.
Proper Formula Preparation
Use distilled or filtered water when mixing powdered formula to prevent digestive upset from minerals or chemicals in tap water[3]. Follow package directions precisely, as formula that’s too concentrated can cause diarrhea, while diluted formula won’t provide adequate nutrition.
Mix only what you’ll use within 24 hours, and store prepared formula in the refrigerator. Discard any leftover formula after feeding sessions to prevent bacterial growth.
Temperature Control
Formula must be warmed to 98-102 degrees Fahrenheit before each feeding[1][3]. This temperature mimics mother cat’s body temperature and ensures comfortable, safe feeding.
Never heat bottles in a microwave, as this creates dangerous hot spots that can burn a kitten’s mouth[1][3]. Instead, use a water bath method:
- Place the bottle in a bowl of warm water
- Test temperature on your wrist before feeding
- Ensure even heating throughout the formula
- Allow cooling if too hot
2. Master Proper Feeding Position and Technique
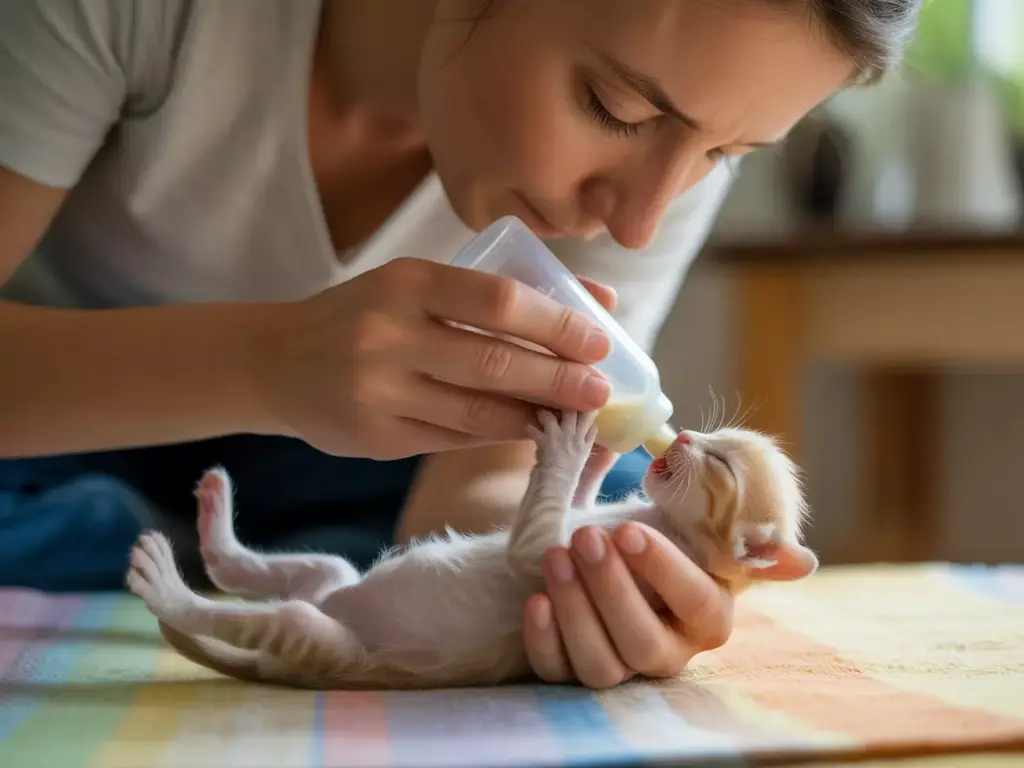

Positioning represents one of the most critical safety aspects when implementing these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro. Incorrect positioning can lead to aspiration pneumonia, a potentially fatal condition.
The Belly-Down Position
Always hold kittens belly-down during feeding, never on their backs or in vertical positions[2][4][5]. This natural position mimics how kittens nurse from their mother and prevents formula from entering the lungs.
Proper positioning technique:
- Support the kitten’s chest with your non-dominant hand
- Keep the head slightly elevated but not tilted back
- Allow all four paws to touch a surface for security
- Maintain gentle but secure grip to prevent squirming
Bottle Angle Management
Maintain the bottle at a 45-degree angle throughout feeding to prevent air ingestion[1][5]. This angle ensures formula flows at an appropriate rate while minimizing the risk of the kitten swallowing air bubbles that can cause digestive discomfort.
Feeding Pace Control
Never squeeze milk into the kitten’s mouth or force feeding, as this significantly increases aspiration risk[4]. Allow kittens to feed at their own pace and take breaks as needed[3].
Signs of proper feeding pace include:
- Steady, rhythmic suckling
- Visible swallowing motions
- Relaxed body posture
- No coughing or choking sounds
Understanding Feeding Schedules and Amounts
Successful implementation of these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro requires understanding how feeding requirements change as kittens grow. Proper scheduling ensures optimal nutrition while preventing overfeeding complications.
Age-Based Feeding Guidelines
| Kitten Age | Formula Amount | Feeding Frequency | Daily Feedings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-1 week | 2-6 mL | Every 2 hours | 12 feedings |
| 1-2 weeks | 6-10 mL | Every 2-3 hours | 8-12 feedings |
| 2-3 weeks | 10-14 mL | Every 3-4 hours | 6-8 feedings |
| 3-4 weeks | 14-18 mL | Every 4-6 hours | 4-6 feedings |
Monitoring Weight Gain
Healthy kittens should gain 10-15 grams daily during their first few weeks of life. Daily weighing helps track progress and adjust feeding amounts accordingly.
Warning signs that may indicate feeding problems:
- ⚠️ No weight gain for 24-48 hours
- ⚠️ Weight loss between feedings
- ⚠️ Lethargy or weakness
- ⚠️ Diarrhea or constipation
- ⚠️ Difficulty breathing during or after feeding
Transitioning to Solid Food
Bottle feeding can typically be discontinued by 6 weeks of age when kittens are eating solid food independently[3]. The weaning process should begin around 4 weeks with the introduction of wet kitten food mixed with formula.
3. Maintain Sterile Equipment and Feeding Environment
Hygiene plays a crucial role in these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro, as newborn kittens have underdeveloped immune systems that make them vulnerable to bacterial infections.
Equipment Sterilization
Clean all feeding equipment thoroughly between uses to prevent harmful bacteria growth. Essential cleaning steps include:
- Rinse immediately after each feeding
- Wash with hot, soapy water using bottle brushes
- Sterilize weekly by boiling for 5 minutes
- Air dry completely before storage
- Replace nipples when they show wear or damage
Feeding Environment Setup
Create a clean, warm, quiet space for feeding sessions. Kittens can become easily stressed by noise, bright lights, or chaotic environments that interfere with their ability to feed properly.
Essential environmental considerations:
- Temperature control – Keep room warm (75-80°F)
- Clean surfaces – Use washable blankets or towels
- Minimal distractions – Reduce noise and activity
- Comfortable seating – Ensure caregiver comfort for longer sessions
Formula Storage Safety
Prepared formula requires careful storage to maintain safety and nutritional value:
- Refrigerate unused formula immediately after preparation
- Use within 24 hours of mixing
- Discard leftover formula from feeding sessions
- Never reuse formula that has been warmed
- Label containers with preparation date and time
4. Recognize and Respond to Feeding Cues

Understanding kitten behavior and feeding cues represents a vital component of these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro. Proper recognition of hunger signals and feeding responses ensures optimal nutrition timing and prevents overfeeding complications.
Hunger Indicators
Healthy, hungry kittens display several clear behavioral signs:
- Vocalization – Crying, mewing, or chirping sounds
- Rooting behavior – Searching motions with head and mouth
- Increased activity – Restless movement or crawling
- Suckling motions – Air suckling or sucking on blankets
- Head bobbing – Seeking motions when touched near the mouth
Satiation Signals
Recognizing when kittens have consumed enough formula prevents dangerous overfeeding:
- Slower suckling – Reduced enthusiasm for the bottle
- Turning away – Head movement away from nipple
- Relaxed posture – Calm, content body language
- Falling asleep – Natural drowsiness after feeding
- Rounded belly – Visible but not distended abdomen
Emergency Warning Signs
Immediate veterinary attention is required if kittens show:
- 🚨 Milk coming from nose – Indicates aspiration risk
- 🚨 Difficulty breathing – Labored or rapid respiration
- 🚨 Blue-tinged gums – Sign of oxygen deprivation
- 🚨 Extreme lethargy – Unresponsiveness to stimulation
- 🚨 Persistent crying – May indicate pain or illness
5. Support Digestion and Elimination
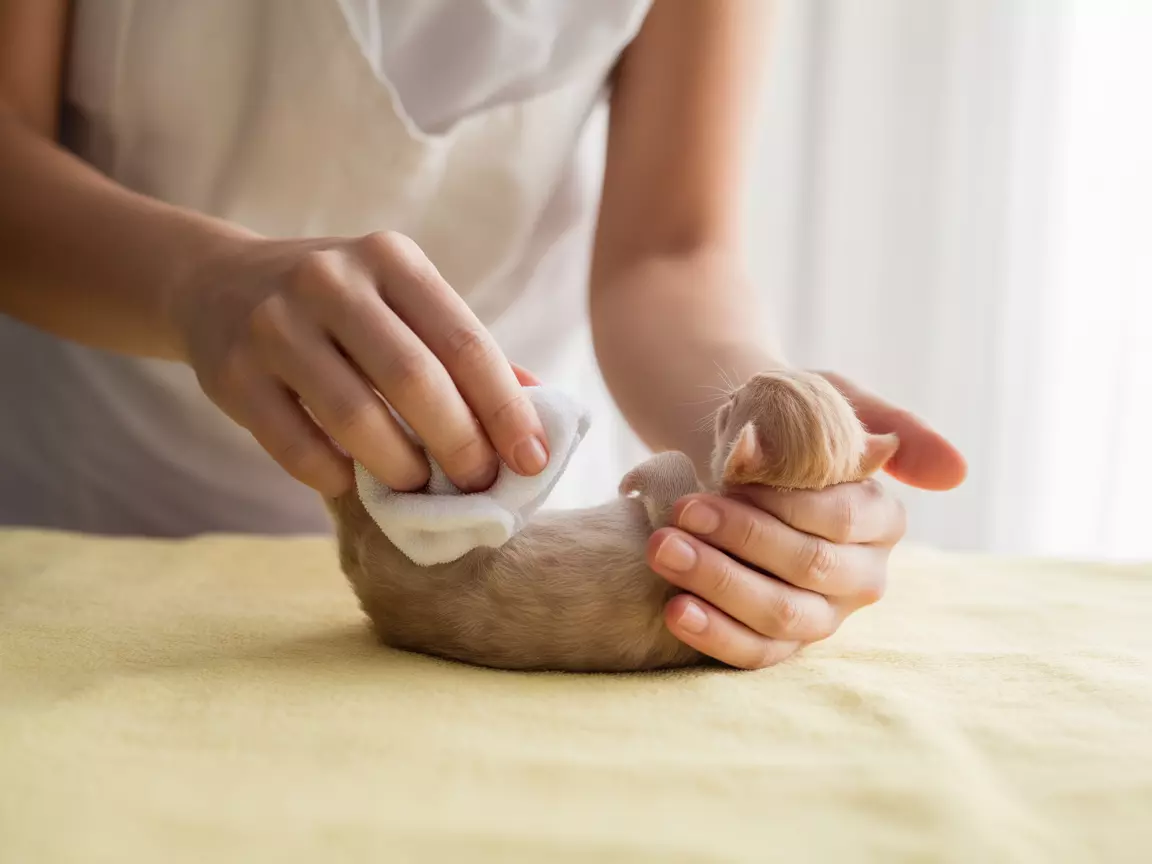

Newborn kittens cannot eliminate waste independently, making digestive support a critical element of these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro. Mother cats naturally stimulate elimination through grooming, a function that hand-rearers must replicate.
Stimulating Elimination
After each feeding, gently stimulate the kitten’s genital and anal areas using a warm, damp cloth or cotton ball. This mimics the mother cat’s tongue action and triggers the elimination reflex.
Proper stimulation technique:
- Use gentle, circular motions around the genital area
- Continue until urination occurs (usually within 30 seconds)
- Stimulate anal area for defecation (may not occur after every feeding)
- Clean thoroughly after elimination
- Dry the area completely to prevent skin irritation
Monitoring Elimination Patterns
Healthy elimination patterns indicate proper digestion:
- Urination – Should occur after most feedings
- Defecation – Every 1-2 days for very young kittens
- Urine color – Pale yellow (dark urine may indicate dehydration)
- Stool consistency – Soft but formed (not liquid or hard)
Digestive Health Support
Several factors support optimal digestion in bottle-fed kittens:
- Consistent feeding schedule – Maintains digestive rhythm
- Proper formula temperature – Aids enzyme function
- Gentle belly massage – Can help with gas and digestion
- Adequate hydration – Prevents constipation
- Stress reduction – Calm environment promotes healthy digestion
6. Monitor Growth and Development Milestones
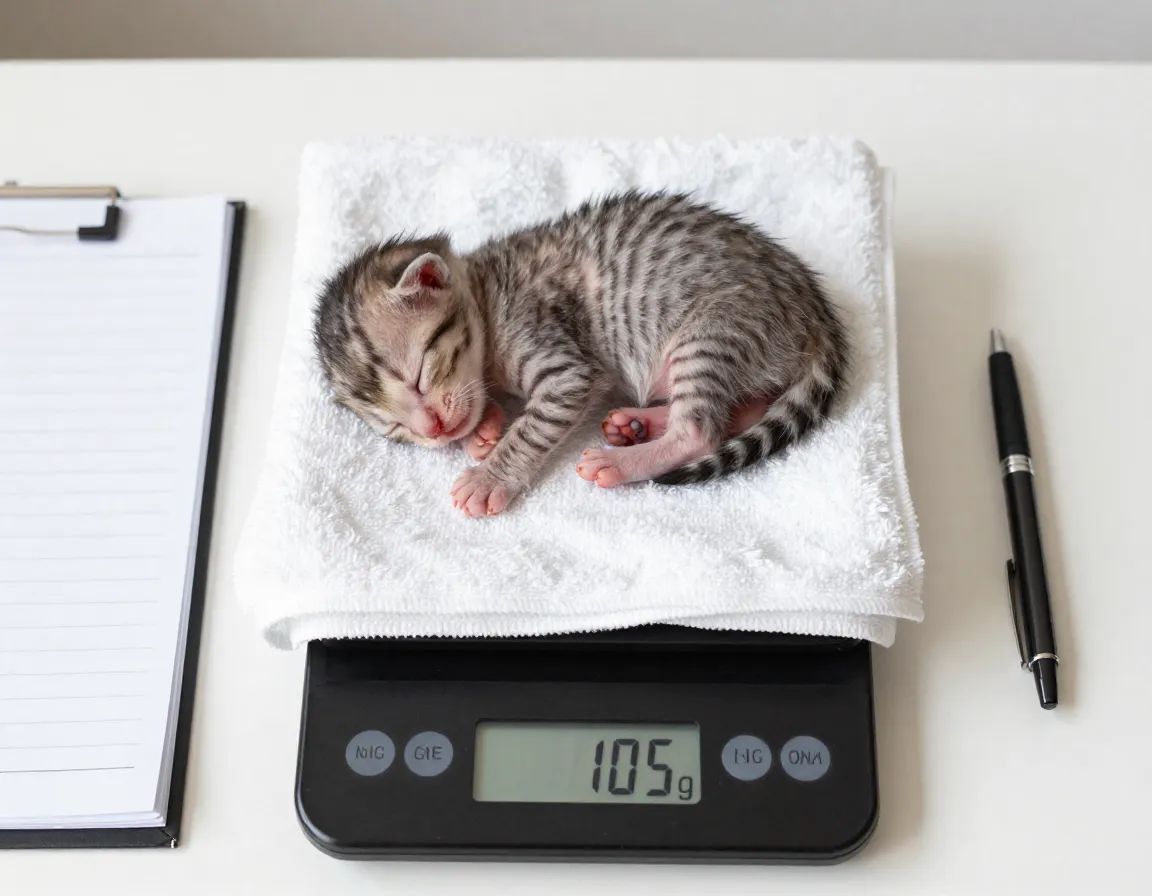

The final component of these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro involves tracking developmental progress to ensure bottle feeding success and identify potential concerns early.
Weight Monitoring
Daily weighing provides the most accurate measure of feeding success. Use a digital kitchen scale capable of measuring in grams for precision.
Expected weight milestones:
- Birth weight – 85-115 grams (3-4 ounces)
- Daily gain – 10-15 grams consistently
- Week 1 – Double birth weight
- Week 2 – 225-250 grams
- Week 4 – 350-450 grams
Developmental Markers
Healthy bottle-fed kittens should meet these developmental milestones:
Week 1:
- Eyes and ears closed
- Limited mobility
- Strong suckling reflex
- Steady weight gain
Week 2:
- Eyes begin opening
- Increased awareness
- Better temperature regulation
- More coordinated movement
Week 3:
- Eyes fully open
- Beginning to walk
- Interest in surroundings
- Starting to groom themselves
Week 4:
- Improved coordination
- Playing with littermates
- Ready for weaning introduction
- Using litter box with assistance
Transitioning to Independence
Successful bottle feeding culminates in healthy, independent kittens ready for adoption. The transition process includes:
- Weaning introduction (4 weeks) – Mix formula with wet food
- Reduced bottle feeding (5 weeks) – Offer bottles 2-3 times daily
- Independent eating (6 weeks) – Eliminate bottle feeding
- Socialization – Interaction with humans and other cats
- Veterinary care – First vaccinations and health check
Troubleshooting Common Feeding Challenges
Even with perfect technique, bottle feeding newborn kittens can present unexpected challenges that require quick problem-solving skills and professional knowledge.
Feeding Refusal
When kittens refuse to take the bottle, consider these solutions:
- Check formula temperature – Too hot or cold formula may be rejected
- Try different nipple types – Some kittens prefer specific nipple shapes
- Assess nipple flow – Holes may be too large or small
- Evaluate kitten health – Illness can cause feeding refusal
- Reduce stress – Create calmer feeding environment
Aspiration Prevention
Aspiration pneumonia represents the most serious risk in kitten bottle feeding. Prevention strategies include:
- Never feed kittens on their backs
- Stop feeding if milk appears at nostrils
- Allow kittens to set their own pace
- Keep head position neutral
- Seek immediate veterinary care if aspiration occurs
Digestive Upset
Formula intolerance or digestive issues may manifest as:
- Diarrhea – May indicate formula concentration problems
- Constipation – Could suggest dehydration or inadequate stimulation
- Bloating – Possible overfeeding or gas accumulation
- Vomiting – May indicate feeding too quickly or illness
Building Long-term Success
Mastering these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro creates the foundation for raising healthy, well-socialized cats that thrive throughout their lives.
Creating Support Networks
Successful kitten bottle feeding often requires support from:
- Veterinary professionals – Regular health monitoring and emergency care
- Experienced foster volunteers – Practical advice and emotional support
- Online communities – 24/7 access to experienced bottle feeders
- Local rescue organizations – Resources and backup care options
Record Keeping
Maintain detailed feeding records including:
- Daily weights – Track growth patterns
- Feeding amounts and times – Monitor intake consistency
- Elimination patterns – Ensure healthy digestion
- Behavioral observations – Note developmental milestones
- Health concerns – Document any issues for veterinary reference
Conclusion
Successfully implementing these 6 Essential Tips for Bottle Feeding Newborn Kittens Like a Pro requires dedication, precision, and unwavering commitment to the highest standards of kitten care. From selecting appropriate formula and mastering feeding positions to monitoring development and supporting digestion, each element plays a crucial role in transforming vulnerable newborns into thriving, healthy cats.
The journey of bottle feeding newborn kittens demands around-the-clock attention, but the rewards of watching helpless babies grow into playful, independent cats make every sleepless night worthwhile. These professional techniques, developed through years of veterinary research and hands-on experience, provide the roadmap for success.
Take action today by gathering necessary supplies, establishing feeding schedules, and connecting with local veterinary professionals who can provide ongoing support. Remember that every kitten’s needs may vary slightly, so remain flexible while maintaining these core principles.
The lives of vulnerable kittens depend on caregivers who understand that bottle feeding requires more than good intentions—it demands professional-level knowledge, consistent execution, and unwavering attention to detail. With these essential tips as your guide, you’re equipped to provide the life-saving care that transforms orphaned kittens into beloved family companions.
References
[1] Bottle Feeding Kittens Comprehensive Guide – https://bestfriends.org/pet-care-resources/bottle-feeding-kittens-comprehensive-guide
[2] Aspca Kitten Bottlefeeding Guide – https://www.aspcapro.org/sites/default/files/2023-06/aspca-kitten-bottlefeeding-guide.pdf
[3] Bottle Feeding Kittens – https://www.chewy.com/education/cat/new-cat/bottle-feeding-kittens
[4] Bottlefeeding – http://www.kittenlady.org/bottlefeeding
[5] Bottle Feeding A Kitten – https://www.petmd.com/cat/general-health/bottle-feeding-a-kitten






