8 Vital Steps on How to Feed Newborn Kittens for Optimal Health
When tiny, helpless kittens arrive without their mother, every feeding decision becomes a matter of life and death. These vulnerable creatures depend entirely on proper nutrition to survive their first critical weeks of life. Understanding the 8 Vital Steps on How to Feed Newborn Kittens for Optimal Health can mean the difference between thriving, healthy cats and tragic loss. Whether you’ve found orphaned kittens or are caring for a litter whose mother cannot nurse, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential knowledge to nurture these precious lives through their most vulnerable stage.

Key Takeaways
- Feeding frequency is critical: Newborn kittens need feeding every 3 hours during their first week, gradually extending intervals as they grow
- Proper formula and portions matter: Use kitten milk replacer with approximately 8 milliliters per ounce of body weight daily, never cow’s milk
- Temperature and technique prevent aspiration: Always warm formula to body temperature and feed slowly to avoid dangerous complications
- Gradual weaning ensures smooth transition: Begin introducing wet food mixed with milk replacer at 3 weeks, completing the transition by 8 weeks
- Professional veterinary guidance is essential: Regular check-ups and weight monitoring ensure optimal growth and early detection of health issues
1. Establish the Proper Feeding Schedule Based on Age

The foundation of successful kitten care lies in understanding that feeding schedules must adapt to the kitten’s developmental stage. Newborn kittens have tiny stomachs and rapid metabolisms, requiring frequent, small meals around the clock.
Birth to 1 Week: Feed every 3 hours, providing 8 feedings per day [3]. This intensive schedule mimics the natural nursing pattern with mother cats and ensures consistent nutrition during the most critical growth period.
1-3 Weeks: Extend feeding intervals to every 4 hours, reducing to 6 feedings per day [3]. As kittens grow, their stomach capacity increases, allowing for slightly larger meals with longer intervals between feedings.
3-4 Weeks: Feed every 5 hours, providing 5 feedings per day [3]. This stage marks the beginning of the weaning transition, as kittens start developing teeth and can begin processing semi-solid foods.
4-5 Weeks: Maintain four to five feedings daily [3], gradually introducing more solid food while continuing bottle feeding as needed.
🕐 Pro Tip: Set multiple alarms throughout the night during the first few weeks. Consistent feeding times help establish healthy growth patterns and prevent dangerous blood sugar drops.
2. Calculate Precise Formula Amounts and Nutritional Requirements
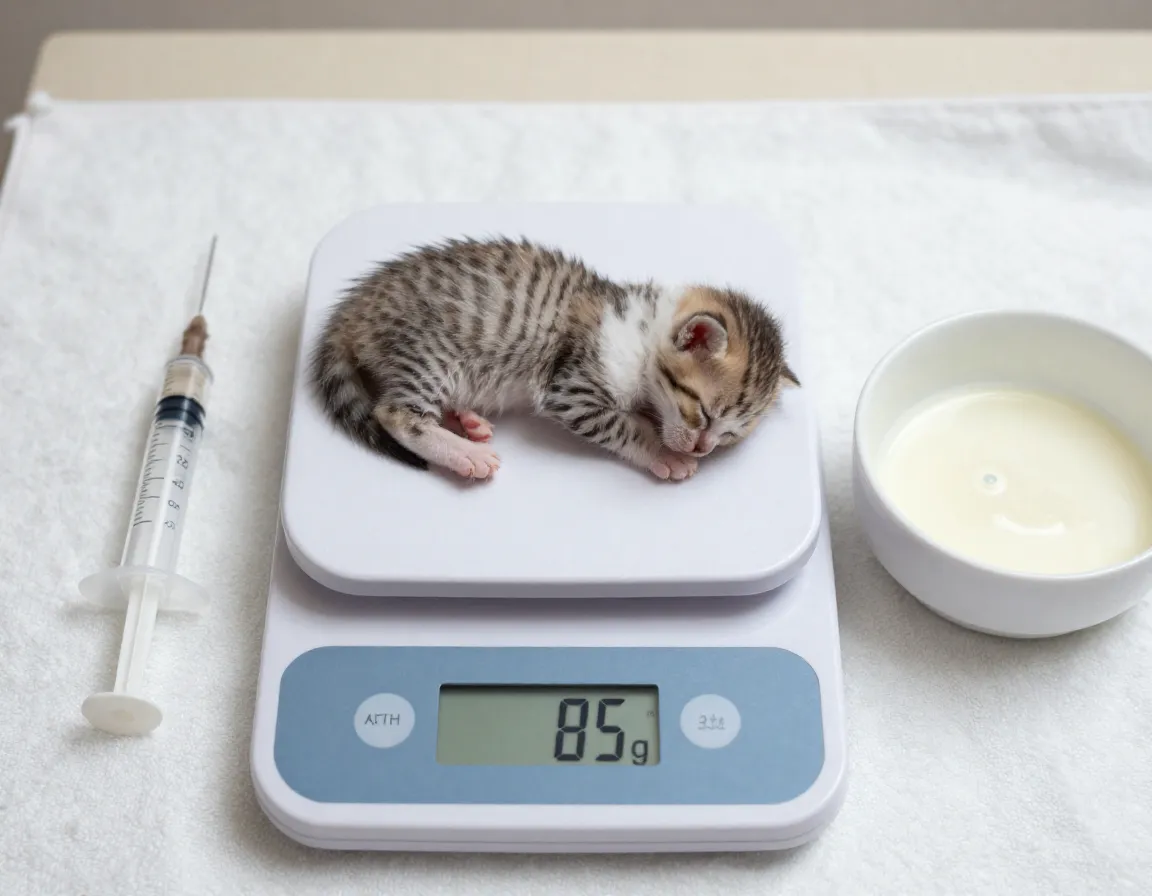
Proper portion control prevents both malnutrition and dangerous overfeeding. Growing kittens require significantly more calories per pound than adult cats, making accurate measurements crucial for healthy development.
Daily Formula Requirements
Kittens require approximately 8 milliliters of formula per ounce of body weight daily [6]. To calculate this:
- Weigh the kitten in ounces
- Multiply weight by 8 to get total daily formula needed
- Divide by number of daily feedings to determine per-meal portions
Caloric Needs
The daily caloric requirement ranges from 20-26 kcal per 100g of body weight [4]. Growing kittens need as much as three times more calories and nutrients than adult cats [2], emphasizing the importance of high-quality kitten milk replacer.
Stomach Capacity Limits
Never exceed 4 ml per 100g of body weight per feeding [4]. Exceeding this maximum comfortable stomach capacity risks:
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Vomiting and regurgitation
- Diarrhea and digestive upset
- Dangerous gas buildup
| Kitten Weight | Daily Formula Amount | Per-Feeding Amount (8 feeds) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 24 ml | 3 ml |
| 4 oz (113g) | 32 ml | 4 ml |
| 5 oz (142g) | 40 ml | 5 ml |
| 6 oz (170g) | 48 ml | 6 ml |
3. Select and Prepare High-Quality Kitten Milk Replacer

The choice of milk replacer directly impacts kitten survival and development. Never use cow’s milk, which lacks essential nutrients and can cause severe digestive problems in kittens.
Commercial Kitten Milk Replacer Features
Quality kitten milk replacers should contain:
- High protein content (minimum 35% dry matter basis)
- Essential fatty acids for brain and eye development
- Appropriate calcium-to-phosphorus ratio for bone growth
- Digestible carbohydrates for energy
- Vitamins and minerals specifically formulated for kittens
Preparation Guidelines
- Follow manufacturer instructions precisely for powder-to-water ratios
- Use warm, filtered water (never hot water that could destroy nutrients)
- Mix thoroughly to eliminate lumps that could clog feeding equipment
- Prepare fresh formula for each feeding session
- Discard unused formula after 1 hour at room temperature
“Proper formula preparation is as critical as feeding frequency. Even small mistakes in mixing ratios can lead to nutritional imbalances that affect long-term health.”
4. Master Safe Feeding Techniques and Equipment
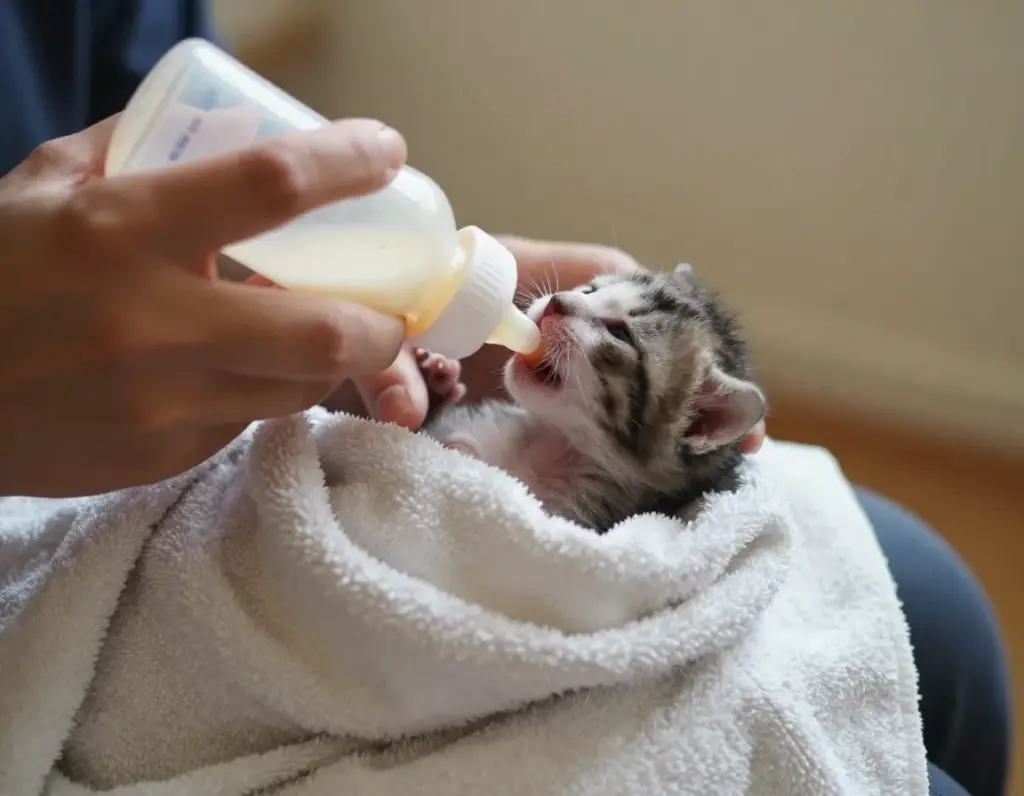

Proper feeding technique prevents aspiration pneumonia, the leading cause of death in bottle-fed kittens. The method matters as much as the formula itself.
Essential Feeding Equipment
- Kitten nursing bottles with appropriate nipple sizes
- Feeding syringes (without needles) for precise control
- Digital scale for monitoring weight gain
- Thermometer for checking formula temperature
- Clean towels for positioning and cleanup
Step-by-Step Feeding Process
- Warm formula to body temperature (100-102°F/38-39°C)
- Position kitten on stomach with head slightly elevated
- Insert nipple gently into the mouth, allowing natural suckling
- Feed slowly – let the kitten control the pace
- Watch for milk bubbles around the nose (sign of proper flow rate)
- Stop immediately if kitten shows distress or formula comes from nose
Warning Signs During Feeding
- Formula coming from nose or mouth
- Gasping or difficulty breathing
- Excessive crying or agitation
- Bloated or distended abdomen
- Lethargy or unresponsiveness
5. Monitor Growth Progress and Adjust Feeding Plans
Consistent weight monitoring ensures kittens receive adequate nutrition and identifies problems early. Healthy kittens should gain weight steadily and show predictable growth patterns.
Daily Weight Tracking
- Weigh kittens daily at the same time using a digital scale
- Record weights in a feeding log or chart
- Expect 10-15g daily weight gain during the first few weeks
- Double birth weight by 10-14 days of age
- Triple birth weight by 3 weeks of age
Growth Milestones
Week 1: Eyes closed, ears folded, weight gain primary indicator of health
Week 2: Eyes begin opening, continued steady weight gain
Week 3: Eyes fully open, ears erect, beginning mobility
Week 4: Increased activity, teeth emerging, ready for weaning introduction
Adjusting Feeding Based on Growth
If weight gain slows or stops:
- Increase feeding frequency
- Check formula concentration
- Evaluate feeding technique
- Consult veterinarian immediately
If excessive weight gain occurs:
- Reduce portion sizes slightly
- Ensure proper formula mixing
- Monitor for signs of overfeeding
6. Begin the Weaning Transition at the Appropriate Time
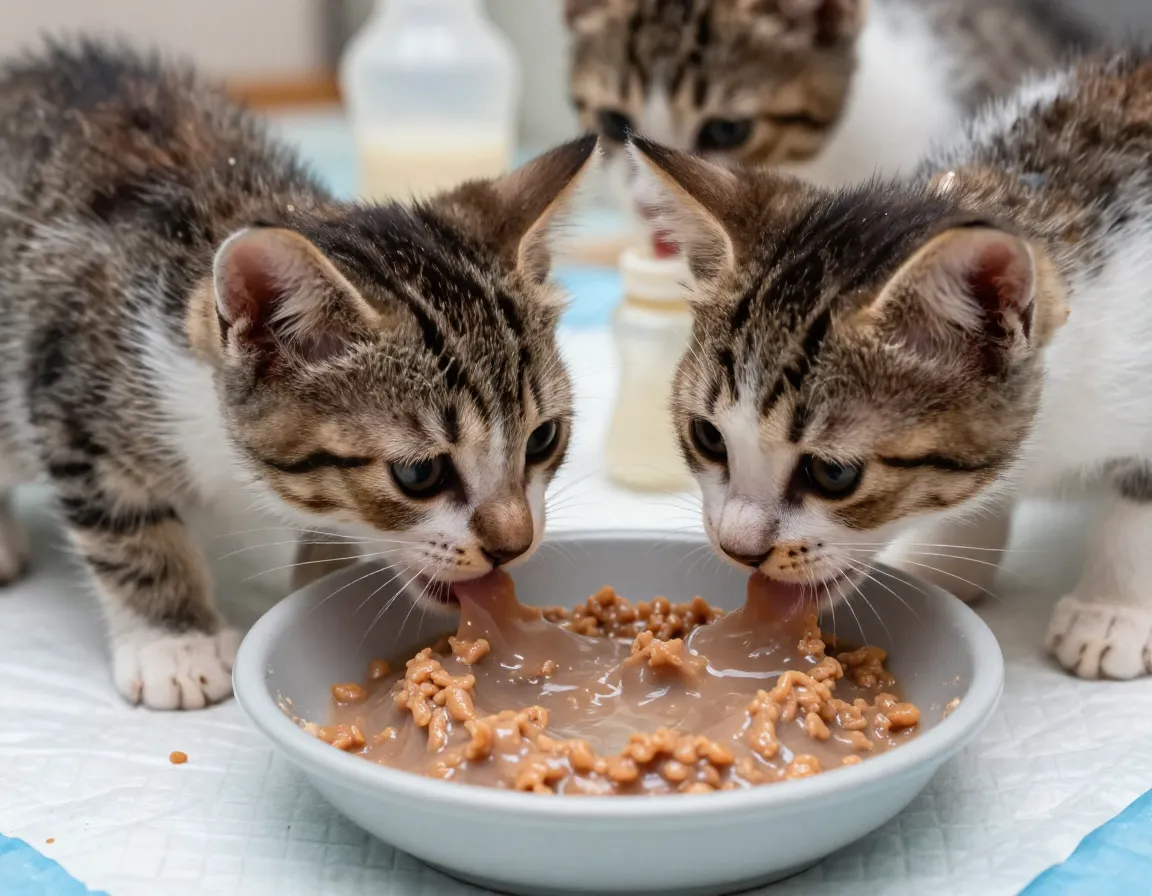

Natural weaning typically begins around 4-6 weeks old [1], but hand-raised kittens may start the transition slightly earlier. This gradual process requires patience and careful observation.
Starting the Weaning Process (3 Weeks)
Begin introducing wet food mixed with kitten milk replacer at 3 weeks old [7]. This creates a familiar taste while introducing new textures:
- Mix high-quality wet kitten food with milk replacer to create a gruel consistency
- Offer small amounts in shallow dishes
- Continue bottle feeding as the primary nutrition source
- Allow exploration – expect messy eating initially
- Clean kittens gently after meals to prevent skin irritation
Progressive Texture Changes
- Week 3-4: Very wet gruel consistency
- Week 4-5: Thicker mixture, less milk replacer
- Week 5-6: Chunky wet food with minimal liquid added
- Week 6-8: Regular wet kitten food and dry kibble introduction
Monitoring the Transition
Watch for:
- Enthusiastic eating of solid foods
- Continued weight gain throughout transition
- Normal elimination patterns
- Reduced interest in bottle feeding
7. Establish Long-Term Nutritional Planning

Proper nutrition extends far beyond the newborn period. Planning for long-term dietary needs ensures continued optimal health as kittens mature into adult cats.
Feeding Schedule Evolution
4-6 Months: Four meals daily of high-quality kitten food
6-12 Months: Three meals daily, continued kitten formula nutrition
After First Year: Switch to adult cat food with veterinary consultation [1]
Nutritional Requirements by Life Stage
Growing kittens need:
- Higher protein levels than adult cats (minimum 30% dry matter)
- Increased fat content for energy and development (minimum 9% dry matter)
- Enhanced vitamin and mineral profiles supporting rapid growth
- Smaller kibble sizes appropriate for developing teeth and jaws
Transitioning to Adult Food
By 8 weeks old, kittens should be fully transitioned to solid kitten food [1]. The eventual switch to adult food should be gradual:
- Begin transition around 10-12 months of age
- Mix increasing amounts of adult food with kitten food over 7-10 days
- Monitor body condition and adjust portions accordingly
- Consult veterinarian for specific timing based on individual development
8. Recognize When to Seek Professional Veterinary Care

Professional veterinary guidance remains essential throughout the feeding process. Recognizing when to seek immediate help can prevent minor issues from becoming life-threatening emergencies.
Immediate Veterinary Attention Required
- Failure to gain weight for more than 24 hours
- Vomiting or diarrhea lasting more than one feeding
- Difficulty breathing or respiratory distress
- Extreme lethargy or unresponsiveness
- Bloated or painful abdomen
- Dehydration signs (skin tenting, dry gums)
- Temperature abnormalities (too hot or cold to touch)
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Schedule appointments for:
- Initial health assessment within 24-48 hours of rescue
- Weekly weight checks during critical growth periods
- Vaccination planning starting around 6-8 weeks
- Spay/neuter consultation for long-term health planning
- Parasite screening and prevention protocols
Building a Veterinary Relationship
Establish care with a veterinarian experienced in:
- Neonatal kitten care and emergency protocols
- Nutritional counseling for growing cats
- Preventive medicine planning
- 24-hour emergency availability for critical situations
“The relationship with your veterinarian begins the moment you take responsibility for orphaned kittens. Early intervention and professional guidance significantly improve survival rates and long-term health outcomes.”
Supporting Optimal Health Beyond Nutrition
While proper feeding forms the foundation of kitten care, additional factors contribute significantly to overall health and development. Environmental conditions, socialization, and preventive care work together with nutrition to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Environmental Considerations
Temperature regulation remains critical for newborn kittens who cannot regulate their own body temperature. Maintain ambient temperatures between 75-80°F during the first few weeks, gradually reducing as kittens develop their own thermoregulation abilities.
Sanitation practices prevent disease transmission and maintain health. Clean feeding equipment thoroughly between uses, maintain clean bedding, and practice proper hand hygiene when handling kittens.
Socialization and Behavioral Development
Human interaction during feeding times helps kittens develop positive associations with people. Gentle handling, soft speaking, and consistent caregiving routines contribute to well-adjusted adult cats.
Litter training typically begins around 4 weeks of age, coinciding with the weaning process. Provide shallow litter boxes with non-clumping litter to prevent ingestion accidents.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing these 8 Vital Steps on How to Feed Newborn Kittens for Optimal Health requires dedication, attention to detail, and unwavering commitment to these vulnerable creatures. From establishing proper feeding schedules and calculating precise nutritional requirements to mastering safe feeding techniques and planning long-term dietary needs, each step builds upon the previous to create a comprehensive care approach.
The journey from helpless newborn to thriving adult cat depends entirely on the quality of care provided during these critical first weeks. Consistent feeding schedules, appropriate nutrition, careful monitoring, and professional veterinary support form the pillars of successful kitten rearing.
Your Next Steps
- Gather essential supplies including kitten milk replacer, feeding equipment, and monitoring tools
- Establish a feeding schedule appropriate for your kitten’s age and weight
- Create a feeding log to track weights, feeding amounts, and developmental milestones
- Schedule veterinary consultation within 24-48 hours of beginning care
- Prepare for the weaning transition by researching high-quality kitten foods
- Build a support network of experienced kitten caregivers and veterinary professionals
Remember that every kitten saved through proper feeding and care represents not just a life preserved, but a future companion whose health and temperament reflect the quality of early nutrition provided. The 8 Vital Steps on How to Feed Newborn Kittens for Optimal Health serve as your roadmap to successful kitten rearing, ensuring these precious lives have the best possible start in their journey to becoming healthy, happy adult cats.
The responsibility of caring for orphaned kittens may seem overwhelming, but with proper knowledge, appropriate supplies, and professional support, the reward of watching helpless newborns grow into thriving cats makes every sleepless night and careful feeding worthwhile. Your commitment to following these vital steps directly impacts not just survival, but the long-term health and quality of life for these remarkable creatures.
References
[1] Kitten Feeding Schedule From Newborn To 1 Year – https://www.kowaligavet.com/paw-print/kitten-feeding-schedule-from-newborn-to-1-year
[2] Set Up A Healthy Feeding Schedule For Your Kitten – https://www.bluebuffalo.com/articles/cat/set-up-a-healthy-feeding-schedule-for-your-kitten/
[3] Kitten Feeding Schedule Growth Chart – https://www.catspyjamas.org/kitten-feeding-schedule-growth-chart/
[4] Kitten%20bottle%20feeding%20and%20stomach%20capacity%20chart – https://www.maddiesfund.org/assets/documents/institute/kitten%20bottle%20feeding%20and%20stomach%20capacity%20chart.pdf
[6] Bottle Feeding Kittens Comprehensive Guide – https://bestfriends.org/pet-care-resources/bottle-feeding-kittens-comprehensive-guide
[7] How Old Is That Kitten Guide Three Weeks – https://www.alleycat.org/resources/how-old-is-that-kitten-guide-three-weeks/






